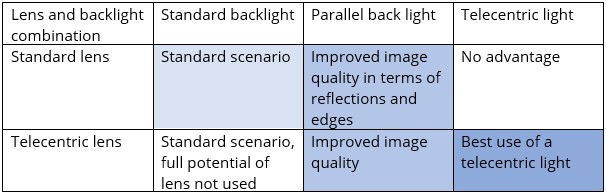
In the world of machine vision systems, achieving accurate and reproduceable image quality is crucial for tasks such as inspection, measurement, and quality control. Telecentric lenses and telecentric lighting play vital roles in enhancing imaging precision. In this article, we will give a brief introduction to telecentric lenses, then delve into the advantages and disadvantages of telecentric lighting. Additionally, we will explore the parallel backlight as an alternative lighting solution in certain scenarios.
If you need any support, or you are interested in our telecentric lenses and lighting, please contact us below. Our website only shows a limited part of our complete portfolio of telecentric lenses and lighting, which can be found here:
Telecentric lens portfolio.
Understanding Telecentric Lenses
Telecentric lenses are optical devices designed to minimize perspective errors and provide consistent magnification and perspective across the entire imaging area. Unlike conventional lenses, telecentric lenses have a unique property where the optical parts are positioned in a special configuration. We offer a variety of telecentric lenses. Our telecentric
lens portfolio and pricing can be found on our website.

Telecentric lenses are designed to have parallel rays entering the lens, resulting in rays that are nearly perpendicular to the image sensor.
This property allows for accurate and consistent measurements as it minimizes perspective errors and distortions. This makes telecentric lenses ideal for precise dimensional measurements and accurate feature extraction. Other features of telecentric lenses are a constant magnification and minimal distortion. Big projects require relatively bigger telecentric lenses:
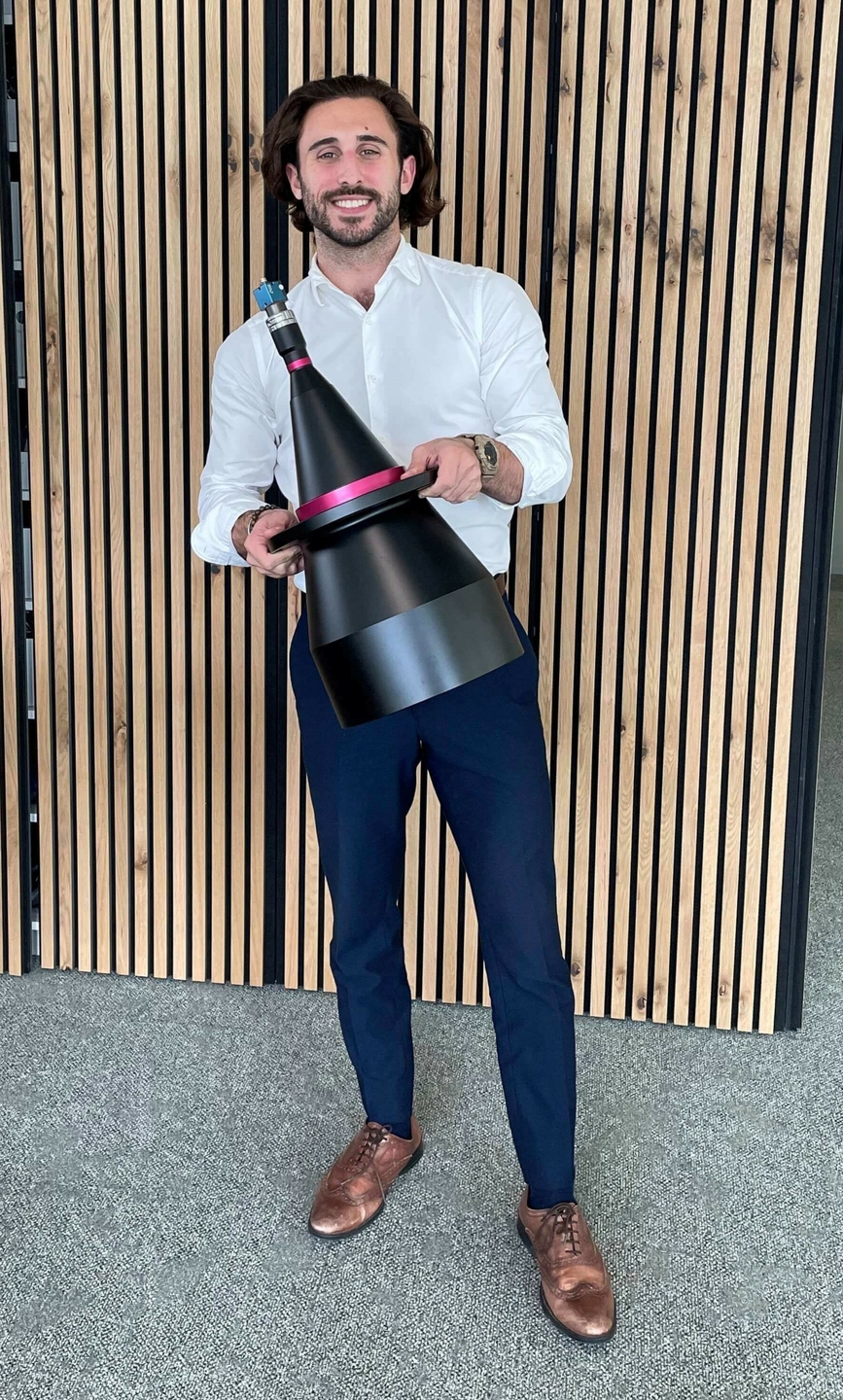 Telecentric lens ; 26cm x 53.5cm ; almost 13kg
Telecentric lens ; 26cm x 53.5cm ; almost 13kg
How Does Telecentric Lighting Work?
Telecentric lighting is an integral part of the telecentric imaging system, working in harmony with telecentric lenses. Unlike conventional back illumination methods where light rays are emitted diffuse or undirected, telecentric lights ensure that the light rays are parallel and have consistent intensity across the entire field of view. This parallel light beam configuration creates silhouettes, minimizes perspective errors and distortion, resulting in accurate measurements and consistent image quality.
To achieve telecentric lighting, the light rays are guided through a sequence of optical elements creating parallel light rays and consistent brightness across the beam. Sometimes this light beam is described as a collimated light beam.
The telecentric light can be considered as a telecentric lens used backwards.
Advantages of Telecentric Lighting
1. Reduced Shadows and Reflections
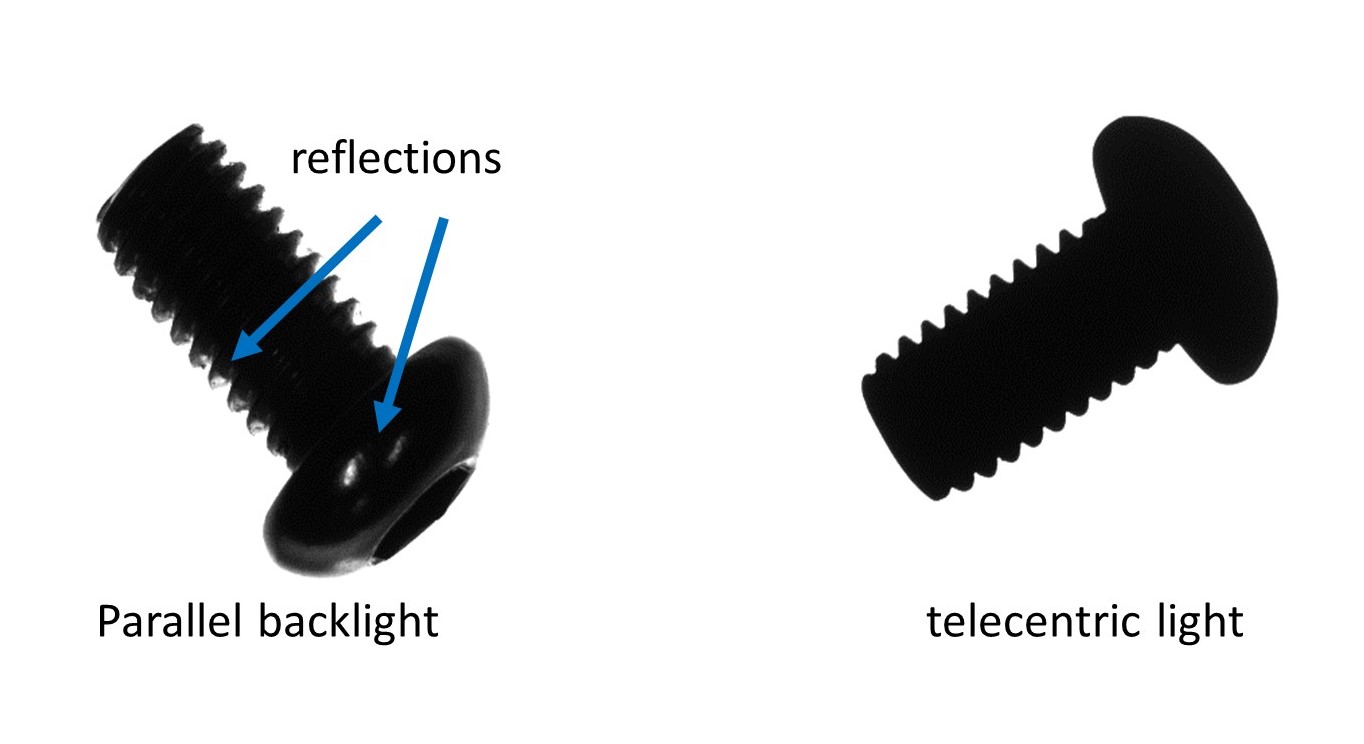
Telecentric lights help minimize shadows and unwanted reflections that can affect image quality and measurement accuracy. With parallel light rays, the potential for shadows caused by the object or the imaging system is reduced.
2. Enhanced Measurement Accuracy
Along with telecentric lenses, a telecentric light helps improve measurement accuracy by reducing errors caused by variations in lighting conditions, perspective distortions, and depth-related effects.
3. Increased Working Distance
It allows larger working distances between the object and the light source. This flexibility is useful in applications where the space between the telecentric light and lens is required for moving or manipulating the product. For example, space required for robot arm movement.
4. Reduced exposure times
The collimated light focused only on the needed area. Therefore the full power of the light source is used. This enables a perfect illumination and high contrast. As a result, short exposure times of the machine vision camera and subsequently short cycle times of the machine.
Challanges of Telecentric Lighting
1. Equipment Cost
Telecentric lighting systems can be more expensive than conventional lighting setups due to the specialized design and precision optics involved. The cost of telecentric lenses and dedicated light sources may pose budgetary challenges for some applications.
2. Space Requirements
The physical size of telecentric lenses and light sources can require additional space in a machine vision setup. This may present limitations in applications where space is restricted or when integrating the lighting system into existing equipment.
3. Installation effort
It's important to note that the use of telecentric lighting will require careful alignment of the optical components. This ensures optimal performance and provides the desired image quality.
Parallel Backlight as an alternative
In situations where space limitations or cost considerations are critical factors,
a parallel backlight can serve as a viable alternative to telecentric lighting. Parallel backlights are equipped with a specialized filter which reduces the diffuse emission of light and creates a more uniform, directed light.
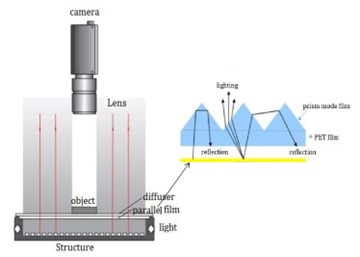
While it may not provide the same level of depth perception or perspective control, a parallel backlight offers advantages in specific scenarios:
1. Space-Saving Solution
Parallel backlighting systems are typically more compact than telecentric lighting setups, making them suitable for applications with limited space constraints or when space optimization is a priority.
2. Uniform Illumination
A parallel backlight, can provide even and uniform illumination across the object's surface. This ensures consistent image quality.
3. Edge Detection and Contrast Enhancement
Parallel backlighting improves edge detection capabilities by enhancing the visibility of object contours and boundaries. It also increases contrast, enabling better differentiation of object features, defects or irregularities.
Conclusion
Systems with telecentric lenses and telecentric lights offer notable advantages in terms of enhanced contrast and measurement precision. While they may involve higher costs and space requirements, the benefits they bring are invaluable. In situations where space limitations or cost considerations are a concern, a parallel backlight can provide a viable/feasable alternative. Parallel backlight offer a uniform illumination and improved edge detection capabilities. When carefully considering the specific requirements and limitations of each lighting technique, machine vision system designers can select the optimal solution for their applications, ensuring reliable and accurate imaging results.